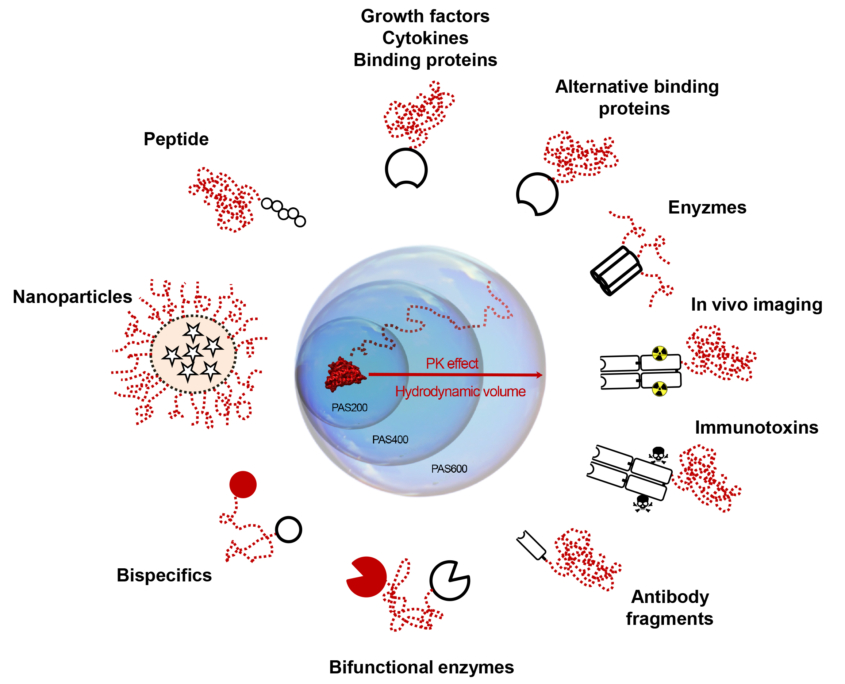
PASylation®-Technology
The genetic fusion with conformationally disordered polypeptide sequences composed of the amino acids Pro, Ala, and/or Ser (‘PASylation’) provides a simple way to attach a solvated random chain with large hydrodynamic volume to the protein of biopharmaceutical interest. This amino acid string adopts a bulky random coil structure, which significantly increases the size of the resulting fusion protein. By this means the typically rapid clearance of the biologically active component via kidney filtration is retarded by 1-2 orders of magnitude, resulting in a long-acting biologic with enhanced action.
PASylation has been successfully applied to a wide range of pharmacologically active drugs including enzymes, cytokines, alternative binding proteins, antibody fragments, peptides, nanocarriers, in vivo imaging tracers, bispecific, ophthalmic and veterinary biologics.